
Published in:
What is a Digital Twin and why is it important for the future of construction?
What is a Digital Twin and Why is it Important for the Future of Construction?
Have you ever wished you could know about a device failure before it happens? Or monitor a building or factory remotely without being physically present? Digital Twin does exactly that! In this article from Payabim, we explain in simple terms what a digital twin is, its applications, and why it should be seriously considered in construction and industrial projects in Iran.What is a Digital Twin? (A Simple Example)
Imagine you have a power plant. Now, create a computer model of this plant that shows all equipment, sensors, and statuses exactly like reality. Even if one of the turbines has a problem, this digital model immediately shows it and alerts you. This model is called a “Digital Twin.” Simple Definition: A digital twin is a digital model of a real object (such as a building, bridge, or industrial machine) that continuously receives updated information and behaves like the real thing.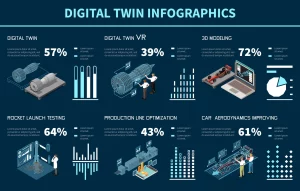
Interesting Statistics About Digital Twins
- 🔹 According to a Gartner report, by 2027 more than 80% of industrial organizations will use digital twins.
- 🔹 Rolls Royce has reduced maintenance costs by 25% using digital twins in aircraft engines.
- 🔹 The UK government has officially been using digital twins in infrastructure projects since 2020 (e.g., Crossrail and Smart Infrastructure).
Why Has the Digital Twin Become Important?
Construction and industrial projects are very expensive, and maintaining them is also costly and complex. If we can see everything before it breaks or control it remotely, both time and money are saved.Key Benefits of Digital Twins:
- ✅ Predictive Alerts: Like having sensors that warn you ahead of problems.
- ✅ Remote Monitoring: You can view project status from home or on your mobile.
- ✅ Accurate Decision-Making: Real data helps you make the right choices.
- ✅ Energy and Cost Savings: Knowing system performance prevents waste.
- ✅ Longer Lifespan: Constant monitoring prolongs the life of structures.
How is a Digital Twin Created?
Creating a digital twin is not difficult but requires coordination. Simple steps:- Digital Modeling (BIM): First, build a 3D model of the building or equipment.
- Install Sensors: Temperature, pressure, sound, or motion sensors are installed on systems.
- Connect to the Internet: Sensor data is sent to a server or software.
- Display in Software: The digital model shows all this information.
- Data Analysis: Use this information for decision-making.
Real Example of Digital Twin Application
In the Crossrail London project, all stations and equipment are controlled using digital models. If there is a leak, malfunction, or delay, it is immediately displayed in the digital model. This made the project 40% faster and 30% cheaper.Why Does Iran Need Digital Twins?
- 🔹 We have thousands of kilometers of bridges, railways, dams, and factories that need careful maintenance.
- 🔹 Most failures are detected late, causing costs and damage.
- 🔹 Digital twins can make projects smart, sustainable, and cost-effective.
Conclusion
A digital twin is not a futuristic technology but a practical and essential tool for better managing today’s projects. If you aim to reduce costs, increase safety, enable smart operation, and make precise decisions, implementing it is a must. ✅ At Payabim, we are ready to help you implement digital twins in your construction and industrial projects. 📞 For free consultation, contact us.What is a Digital Twin and Why is it Critical in Construction Projects?
The world of construction is changing. Building a structure or bridge is not enough; you need to control, maintain, and even predict its condition throughout its life! This is where Digital Twin comes into play. In this article from Payabim, we explain simply what a digital twin is, why it is important, how it works, and how it can be applied in Iran’s construction and industrial projects.What is a Digital Twin?
Imagine having a digital version of a building, bridge, or factory that behaves exactly like the real one. Everything that happens in the real world is reflected in the digital model—like a smart mirror. This digital version uses live sensor data to show changes and even predict the future.Simply put: A digital twin is a live, digital model of a real asset that is always up-to-date and behaves exactly like the real asset.
Benefits of Digital Twins for Projects
- Cost Savings: Repair the system before it breaks; i.e., preventive maintenance.
- 24/7 Monitoring: Like having a third eye on the structure for constant observation.
- Accurate Decision-Making: Based on real data, reducing the risk of mistakes.
- Better Maintenance Management: Plan time, budget, and personnel more accurately.
- Risk Reduction: Quickly detect leaks or settlement in bridges.
Why is a Digital Twin Essential for Iran?
Many large construction projects in Iran, such as metro, bridges, railways, and factories, require precise maintenance. Lack of real-time information increases repair costs and damages. Digital twins allow you to foresee problems and prevent them. Example: If you have a factory with sensitive equipment, a digital twin tells you when to replace filters before machines overheat!How is a Digital Twin Built?
- Initial Digital Modeling (BIM): Create an accurate 3D model with correct information.
- Install Sensors and Collect Data: Such as temperature, vibration, humidity, pressure, energy consumption, etc.
- Connect the Model to Live Data: The digital model updates with real-time information.
- Use Analytics Software: Analyze and predict data, possibly with AI.
- Display on Dashboard: Project managers can see everything on mobile or laptop.
What is Needed to Get Started?
- Accurate BIM or CAD model
- Appropriate sensors (IoT)
- Data analytics platform (e.g., Azure, Siemens, Dassault)
- Professional team (BIM + IT + Engineering)
Real-World Applications of Digital Twins
- Smart Buildings: Control energy, lighting, ventilation
- Bridges and Tunnels: Monitor vibration, settlement, cracks
- Factories: Continuous performance monitoring of machinery

